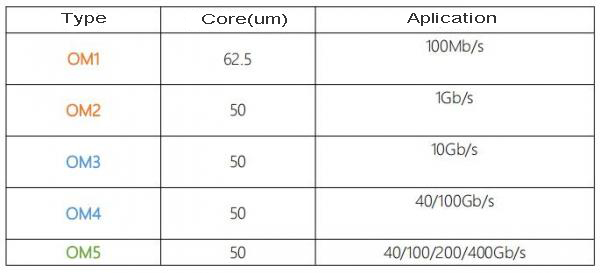
In optical communication, "OM" refers to "Optical Multi mode", which is a standard for representing the fiber grade of multimode optical fibers. At present, the fiber optic jumper standards defined by TIA and IEC include OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5.
Firstly, what are multimode and single-mode?
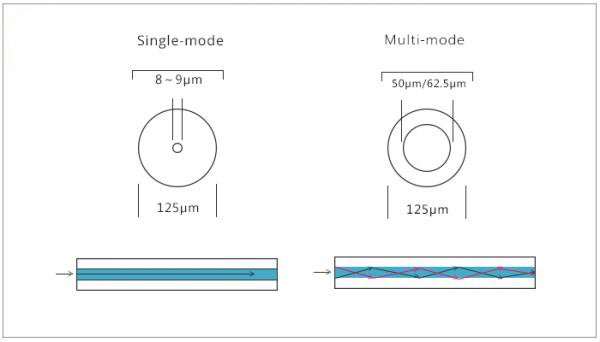
Single Mode Fiber is an optical fiber that allows only one mode of transmission, with a core diameter of approximately 8-9 μ m and an outer diameter of approximately 125 μ m. Multimode optical fiber allows different modes of light to be transmitted on one fiber, with core diameters of 50 μ m and 62.5 μ m. Single mode fiber can support longer transmission distances compared to multimode fiber, and can support transmission distances of over 5000m in 100Mbps Ethernet and even 1G gigabit networks. Multimode fiber is only suitable for medium to short distance and small capacity fiber optic communication systems.
What is the difference between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5?
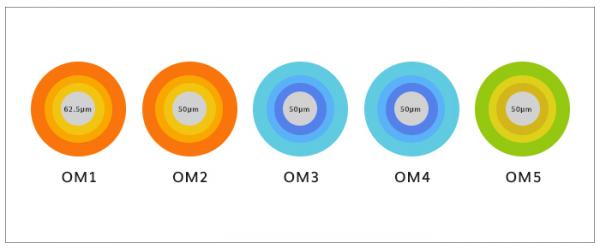
Generally speaking, OM1 is a conventional 62.5/125um; OM2 is a conventional 50/125um; OM3 is a 50um core diameter multimode fiber optimized for 850nm laser. In 10Gb/s Ethernet using 850nm VCSEL, the fiber transmission distance can reach 300m; OM4 is an upgraded version of OM3, which optimizes the differential mode delay (DMD) generated by OM3 multimode fiber during high-speed transmission, thus greatly improving the transmission distance, and the fiber transmission distance can reach 550m; OM5 fiber jumper is a new standard for fiber jumpers defined by TIA and IEC, with a fiber diameter of 50/125 μ m. Compared with OM3 and OM4 fiber jumpers, OM5 fiber jumper can Used for applications with higher bandwidth. The bandwidth and maximum distance for different levels of transmission are different.
What is OM5 fiber optic jumper?
OM5 fiber, also known as broadband multimode fiber patch cord (WBMMF), is a laser optimized multimode fiber (MMF) that specifies bandwidth characteristics specifically for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). The purpose of this new fiber classification method is to provide support for multiple "short" wavelengths between 850nm and 950nm, which are suitable for high bandwidth applications after aggregation. The design of OM3 and OM4 is mainly aimed at supporting a single wavelength of 850nm.
What is the difference between OM3 and OM4?
1. Different sheath colors
To distinguish different fiber jumpers, use outer sheaths of different colors. For non military purposes, single-mode optical fibers generally use a yellow outer sheath. OM1 and OM2 in multimode fiber are orange, OM3 and OM4 are navy blue, and OM5 is navy green.
2. Different application scopes
OM1 and OM2 have been widely deployed in applications inside buildings for many years, supporting Ethernet transmission up to 1GB; OM3 and OM4 optical cables are commonly used in data center cabling environments, supporting transmission over 10G or even 40/100G high-speed Ethernet routes. OM5 is designed for 40Gb/s and 100Gb/s transmission, reducing the number of optical fibers required for high-speed transmission.
Characteristics of OM5 multimode fiber
1. Fewer fibers support higher bandwidth applications
The working wavelength of OM5 fiber optic jumper is 850/1300nm, and it can support at least 4 wavelengths. The typical operating wavelengths of OM3 and OM4 are 850nm and 1300nm. This means that traditional OM1, OM2, OM3, and OM4 multimode fibers only have one channel, while OM5 has four channels, increasing transmission capacity by four times. By combining short wave division multiplexing (SWDM) and parallel transmission technology, OM5 only requires 8-core broadband multimode fiber (WBMMF) to support 200/400G Ethernet applications, greatly reducing the number of fiber cores and significantly lowering network cabling costs.
2. Longer transmission distance
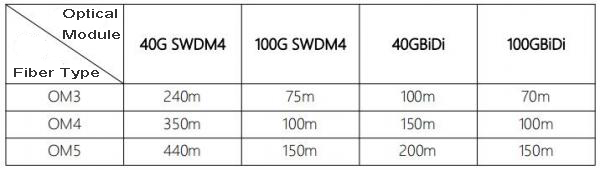
The transmission distance of OM5 fiber optic is longer than that of OM3 and OM4. OM4 fiber is designed to support lengths of at least 100 meters and 100G-SWDM4 transceivers. But OM5 fiber optic can support lengths up to 150 meters with the same transceiver.
3. Lower fiber loss
The attenuation of OM5 broadband multimode optical cable has been reduced from the previous 3.5 dB/km of OM3 and OM4 optical cables to 3.0 dB/km, and the bandwidth requirement at 953nm wavelength has been increased.
OM5 has the same fiber size as OM3 and OM4, which means it is fully compatible with OM3 and OM4. If OM5 is to be used in existing cabling applications, no changes are required. OM5 fiber is more scalable and flexible, capable of supporting faster network transmission with fewer multi-mode fiber cores, and has much lower cost and power consumption than single-mode fiber. Therefore, it will be widely used in 100G/400G/1T ultra large data centers in the future.